About Peltier
What is a Peltier element?
A Peltier device is generally an electronic component that has cooling and heating effects.
The definition of the Peltier effect is “when an electric current flows through the junction of two different metals, heat is transferred from one metal to the other, resulting in cooling (or heating); reversing the current causes the effect to reverse.”
As an advantage,
- There are no moving parts, and it does not generate noise.
- A cooling device that is environmentally friendly and does not cause air pollution (carbon dioxide emissions).
- Both heating and cooling are possible.
To explain in more detail,
In the late 19th century, a scientist named J.C.A. Peltier from France announced this effect, which was named after him as the Peltier effect. It is also commonly referred to as the Seebeck effect.The Seebeck effect, discovered in 1821 by the German scientist Seebeck, refers to the phenomenon where a temperature difference causes an electric current to flow through a metal. It is also known as the Thomson effect, which describes the heating and cooling that occurs when an electric current flows through a conductor with a temperature gradient, and it was discovered by the British physicist William Thomson.
What is the difference between our product and those from other companies?
The Peltier modules from Sensor Controls go through a completely different manufacturing process compared to overseas Peltier modules and those from other domestic manufacturers,resulting in differences in internal structure.
A typical Peltier module maintains its shape by sandwiching two P/N semiconductor elements between. However, Sensor Controls has successfully developed a unique semiconductor technology that allows for the central placement and fixation of a single substratein between two supports.
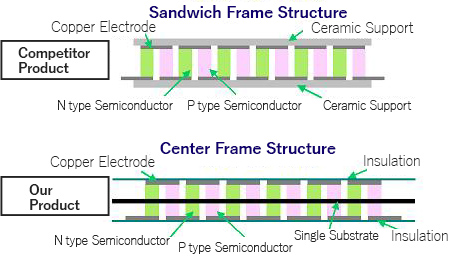
What are the benefits?
The heat generated by the P/N semiconductor element is directly transferred to the aluminum surface, increasing the heat transfer rate. Additionally, the support positioned in the center acts as a heat absorber, providing high resistance to thermal stress, resulting in a product that does not degrade and has a long lifespan.
Verification: Repeated cooling and heating tests were conducted at temperatures ranging from 10°C to 100°C, and there were no changes in quality data even after 500,000 cycles.
Comparison table
| Item | Other companies’ Peltier elements | Our company’s Peltier element |
| Raw materials | Bismuth, Antimony, Tellurium (Bi、Sb、Te)Compound |
Bismuth, Antimony, Tellurium (Bi、Sb、Te)Compound |
| Characteristics of the manufacturing method | More waste of raw materials(~60%) | Less waste of raw materials.(~10%) |
| Material characteristics |  |
 |
| Characteristics of manufacturing methods and elements | ■Three cutting processes and a lot of material waste. ■Fragile due to its rigid structure. ■Unable to perform ON/OFF control (rapid cooling). ■Low reliability ■Due to the rigid structure, the cooling capacity (COP) has not changed in the last 20 to 30 years. |
■One cutting process with minimal material waste. ■It does not break due to its flexible structure. ■ON/OFF control (rapid cooling) is possible. ■Highly reliable ■The cooling capacity (COP) of the single crystal element is improved by 25% compared to the Peltier element. |
| Developability | The use is limited. There is no path to widespread adoption with a manufacturing method that discards over 80% of the material. | The disposal of materials is below 20%, performance improvement of components, outstanding reliability, and cost reduction in mass production will open the way for widespread adoption. |




